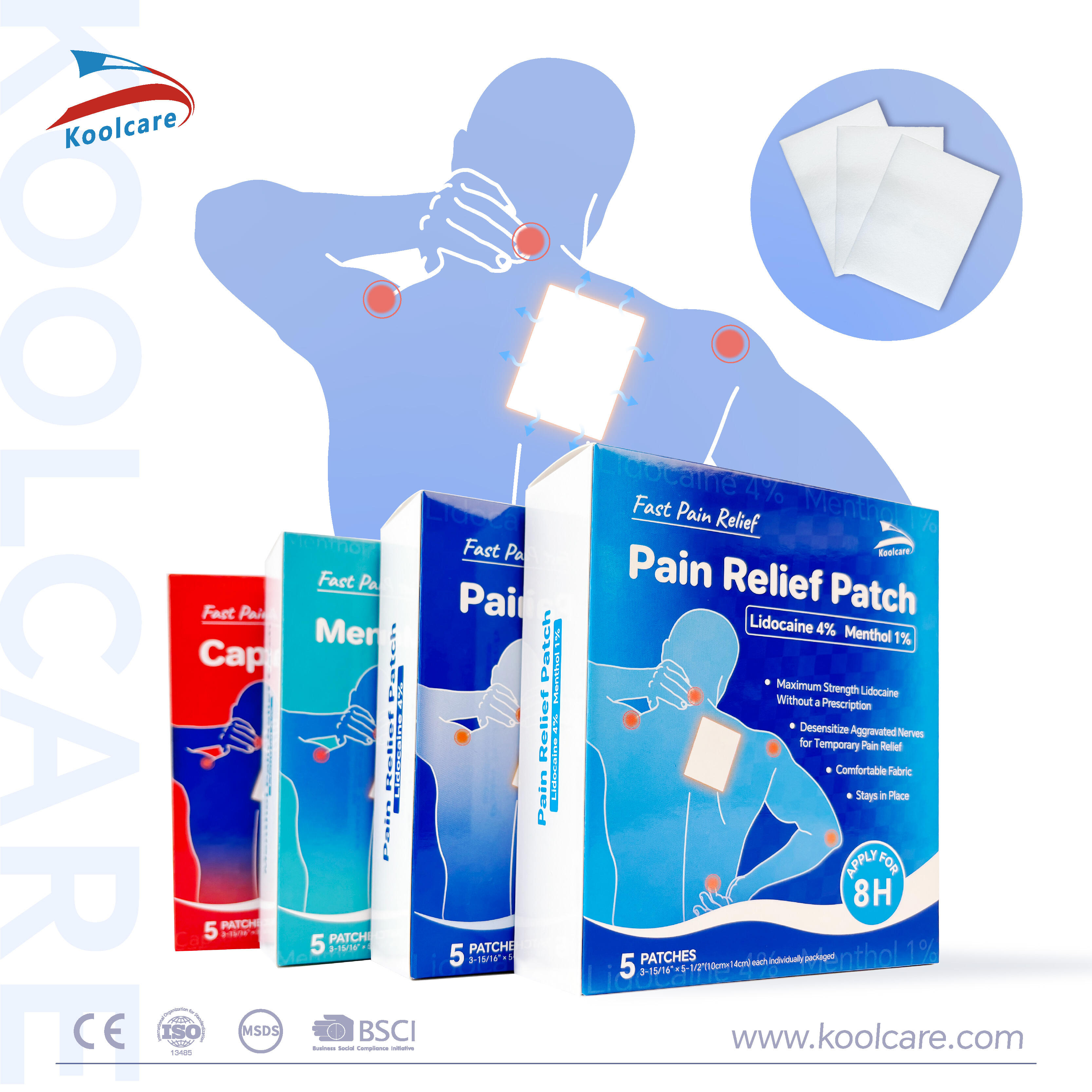
Chronic muscle and joint discomfort affects millions of people worldwide, driving the search for effective and convenient treatment options. Traditional oral medications and topical creams have long been the standard approach, but innovative transdermal solutions are revolutionizing how we address localized pain. Among these emerging therapies, pain relief patches have gained significant attention for their targeted delivery system and sustained therapeutic benefits. These advanced patches offer a non-invasive alternative that delivers active ingredients directly through the skin to affected areas, providing consistent relief without the systemic side effects often associated with oral pain medications.

The mechanism behind transdermal patch technology represents a sophisticated approach to pain management that bypasses the digestive system entirely. Unlike oral medications that must be processed through the liver and stomach, patches deliver therapeutic compounds directly through dermal absorption. This targeted delivery method ensures higher bioavailability at the site of discomfort while minimizing potential gastrointestinal complications. Modern patch formulations incorporate advanced hydrogel matrices and permeation enhancers that facilitate optimal drug penetration through the skin barrier, creating a reservoir effect that maintains consistent therapeutic levels over extended periods.
Understanding Transdermal Pain Management Technology
Advanced Delivery Systems in Modern Patches
Contemporary transdermal patches utilize sophisticated polymer matrices that control the release rate of active pharmaceutical ingredients. These systems employ multilayer designs incorporating backing films, drug reservoirs, adhesive layers, and protective liners that work synergistically to ensure optimal therapeutic delivery. The hydrogel technology commonly used in premium patches provides excellent skin adhesion while maintaining moisture balance, preventing irritation during extended wear periods. Advanced formulations can maintain therapeutic drug levels for up to eight hours or longer, depending on the specific compound and delivery system design.
Bioavailability and Absorption Mechanisms
The skin's stratum corneum presents a natural barrier that transdermal systems must overcome to achieve therapeutic efficacy. Modern patches incorporate chemical enhancers and physical modification techniques that temporarily increase skin permeability without causing damage. Iontophoresis, microneedles, and specialized carrier molecules facilitate deeper penetration of active ingredients. The subcutaneous tissue beneath the application site becomes a localized reservoir, allowing for sustained release and targeted action. This localized delivery approach results in higher concentrations at the treatment site compared to systemic administration methods.
Clinical Applications for Muscle and Joint Discomfort
Targeted Relief for Specific Conditions
Musculoskeletal conditions respond particularly well to transdermal therapy due to the proximity of affected tissues to the skin surface. Conditions such as arthritis, sports injuries, repetitive strain injuries, and chronic back pain benefit from the sustained delivery that patches provide. The localized nature of patch therapy makes it especially effective for joint-related discomfort where oral medications might not achieve adequate concentrations. Clinical studies demonstrate significant improvement in pain scores and functional mobility when patches are used as part of comprehensive treatment protocols.
Advantages Over Traditional Treatment Methods
Transdermal patches offer several distinct advantages over conventional oral analgesics and topical preparations. The controlled release mechanism provides consistent therapeutic levels without the peak-and-trough variations associated with oral dosing. Patients experience improved compliance due to the convenience of once-daily or less frequent application schedules. The reduced systemic exposure minimizes potential side effects such as gastrointestinal irritation, liver stress, and drug interactions. Additionally, patches remain effective even when patients have difficulty swallowing medications or experience nausea that interferes with oral therapy.
Composition and Active Ingredients
Pharmaceutical Compounds in Modern Patches
Contemporary pain relief patches incorporate various classes of therapeutic compounds designed for transdermal delivery. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, topical analgesics, natural extracts, and novel synthetic compounds are formulated specifically for percutaneous absorption. Menthol and camphor provide immediate cooling sensations while deeper-acting ingredients address underlying inflammatory processes. Some patches combine multiple active ingredients to provide both immediate and sustained relief through different mechanisms of action.
Hydrogel Matrix Technology
The hydrogel matrix serves as the foundation for modern patch technology, providing optimal drug release characteristics and skin compatibility. These biocompatible polymers maintain moisture content while allowing controlled diffusion of therapeutic agents. The gel structure adapts to body contours and movement, ensuring consistent contact and drug delivery even during physical activity. Advanced hydrogel formulations incorporate pH buffering systems and stabilizing agents that maintain drug potency throughout the patch's intended wear time. The matrix also includes adhesive components that provide secure attachment without causing skin irritation upon removal.
Application Techniques and Best Practices
Proper Placement and Skin Preparation
Effective patch therapy requires proper application techniques to maximize therapeutic benefits and minimize potential complications. The target area should be clean, dry, and free from lotions, oils, or other topical preparations that might interfere with adhesion or absorption. Hair removal may be necessary in certain areas to ensure proper contact, but should be done with care to avoid skin irritation. The patch should be applied with firm pressure and held in place for several seconds to ensure complete adhesion. Placement directly over the area of discomfort typically provides optimal results, though some systemic patches may be applied to alternative sites.
Duration of Use and Safety Considerations
Most therapeutic patches are designed for specific wear times ranging from several hours to multiple days, depending on the active ingredients and intended therapeutic goals. Exceeding recommended wear times may lead to skin irritation or reduced efficacy due to depleted drug reservoirs. Patients should monitor the application site for signs of allergic reactions, excessive redness, or irritation that persists beyond normal expectations. Rotation of application sites helps prevent skin sensitization and maintains optimal absorption capacity. Healthcare providers should establish clear guidelines for patch replacement schedules and monitoring protocols.
Effectiveness and Clinical Evidence
Research Supporting Transdermal Therapy
Extensive clinical research demonstrates the efficacy of transdermal patches for managing various types of musculoskeletal pain. Randomized controlled trials show comparable or superior pain reduction when patches are compared to oral medications for localized conditions. Patient-reported outcomes consistently indicate improved quality of life, reduced interference with daily activities, and enhanced sleep quality. Long-term studies reveal sustained benefits without the tolerance issues sometimes associated with systemic pain medications. The evidence base continues to expand as new formulations and delivery technologies are developed and tested.
Comparative Analysis with Other Treatment Modalities
When compared to traditional treatment approaches, transdermal patches demonstrate unique advantages in specific clinical scenarios. For patients with gastrointestinal sensitivities or those taking multiple oral medications, patches provide effective therapy without adding to pill burden or interaction risks. The localized delivery achieves therapeutic concentrations at target tissues while maintaining lower systemic levels compared to oral administration. This pharmacokinetic profile makes patches particularly valuable for elderly patients or those with compromised organ function who may be more susceptible to medication-related adverse effects.
Safety Profile and Considerations
Common Side Effects and Management
Transdermal patches generally exhibit favorable safety profiles with most adverse effects limited to the application site. Mild skin reactions such as redness, itching, or temporary discoloration occur in a small percentage of users and typically resolve quickly after patch removal. More significant reactions are rare but may include contact dermatitis or allergic sensitization to patch components. Proper skin preparation, appropriate patch selection, and adherence to recommended wear times minimize the risk of complications. Healthcare providers should educate patients on recognizing and managing potential side effects while emphasizing the importance of discontinuing use if severe reactions develop.
Contraindications and Special Populations
Certain patient populations require special consideration when using transdermal patches for pain management. Individuals with compromised skin integrity, active dermatological conditions, or known allergies to patch components may not be suitable candidates. Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult healthcare providers before using medicated patches due to potential systemic absorption. Pediatric use requires careful consideration of patch size, drug concentration, and application site to ensure safety and efficacy. Patients with temperature sensitivity or those exposed to external heat sources should understand how thermal effects might alter drug release rates.
FAQ
How long do pain relief patches typically provide effective relief
Most modern pain relief patches are designed to provide consistent therapeutic benefits for 8 to 12 hours, with some advanced formulations extending up to 24 hours. The duration depends on the specific active ingredients, patch design, and individual patient factors such as skin permeability and metabolic rate. Patches using sustained-release technology maintain steady drug levels throughout their intended wear time, avoiding the fluctuations common with oral medications. For optimal results, patients should follow manufacturer guidelines and replace patches according to the recommended schedule rather than waiting for pain to return.
Are pain relief patches safe for long-term daily use
Long-term use of pain relief patches is generally considered safe when used according to medical guidance and manufacturer recommendations. The localized delivery system reduces systemic exposure compared to oral medications, potentially decreasing the risk of organ-related side effects. However, prolonged use requires monitoring for skin sensitization and the development of contact allergies. Patients should rotate application sites to prevent skin irritation and maintain regular follow-ups with healthcare providers to assess continued need and effectiveness. Some patches are specifically formulated for chronic conditions and designed for extended use protocols.
Can pain relief patches be used alongside other pain medications
Pain relief patches can often be safely combined with other pain management therapies, but medical supervision is essential to prevent drug interactions and ensure appropriate dosing. The reduced systemic absorption of transdermal medications typically decreases interaction risks compared to multiple oral drugs. However, patients should inform healthcare providers about all medications, supplements, and topical treatments being used concurrently. Some combinations may provide synergistic benefits, while others might require dose adjustments or timing modifications. A comprehensive pain management plan should coordinate all therapeutic approaches for optimal safety and efficacy.
What should I do if the patch causes skin irritation
Mild skin irritation such as slight redness or itching at the application site is relatively common and often resolves with proper patch management. If irritation occurs, remove the patch immediately and gently clean the area with mild soap and water. Allow the skin to recover completely before considering reapplication to a different site. Persistent or severe reactions including blistering, intense burning, or spreading rash require immediate medical attention. Future patch use may require switching to different formulations with alternative adhesives or active ingredients. Patients with sensitive skin should discuss patch options with healthcare providers to select the most appropriate products.